$y=\dfrac{e^x-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}}$ という関数を双曲線正接、またはハイパボリックタンジェントと言う。記号では $\tanh x$ と書く。
tanh xの極限
$\displaystyle\lim_{x\to\infty}\tanh x=1$ が成立します。
~証明~
$\tanh x=\dfrac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}}=\dfrac{1-e^{-2x}}{1+e^{-2x}}$ と変形できます。
$x\to\infty$ のとき $e^{-2x}\to 0$ となるので $\tanh x$ は $1$ に収束します。
$\displaystyle\lim_{x\to -\infty}\tanh x=-1$ が成立します。
~証明~
$\tanh x=\dfrac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}}=\dfrac{e^{2x}-1}{e^{2x}+1}$ と変形できます。
$x\to -\infty$ のとき $e^{2x}\to 0$ となるので $\tanh x$ は $-1$ に収束します。
tanh xの微分
$(\tanh x)’=\dfrac{4}{(e^x+e^{-x})^2}=\dfrac{1}{\cosh^2 x}$ が成立します。
~証明~
商の微分公式より、
$(\tanh x)’\\
=\left(\frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}}\right)’\\
=\dfrac{(e^x+e^{-x})^2-(e^x-e^{-x})^2}{(e^x+e^{-x})^2}\\
=\dfrac{4}{(e^x+e^{-x})^2}$
さらに、$\cosh x=\dfrac{e^x+e^{-x}}{2}$ であることを使うと、上式は $\dfrac{1}{\cosh^2 x}$ と書くこともできます。
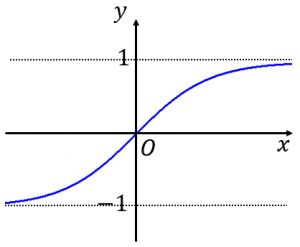
tanh xのグラフ、漸近線
$\tanh x$ のグラフは図のようになることが分かります。

~ポイント~
・$x\to\infty$ で $\tanh\to 1$
・$\tanh (-x)=-\tanh x$ なので奇関数、つまり、原点を通る、かつ原点対称
・$y=1$ および $y=-1$ が漸近線
tanh xの不定積分
$\displaystyle\int\tanh xdx=\log(e^x+e^{-x})+C$ が成立します。
これは、$\displaystyle\int \dfrac{f'(x)}{f(x)}dx=\log|f(x)|+C$ という積分公式で $f(x)=e^x+e^{-x}$ とすれば導出できます。
次回は sech、csch、cothの意味、微分、積分 を解説します。